The lab focuses on the two key paradigms in the combinatorial library approach, namely, the combination / recombination vs. elimination / selection of a natural repertoire using the principle of evolution. In particular, our current research direction is to design and establish suitable phenotypic screening methods in cells and insects (animals) to identify novel antibodies with specific functions and biological activities from the available high diversity (1x10E11) antibody combinatorial library. Our main research interest is in the fields of tumor immunology, metabolic diseases, and rare genetic diseases, associated with gap junction channels mutation.
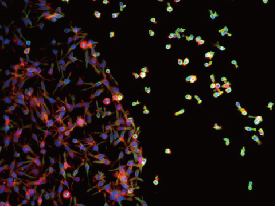
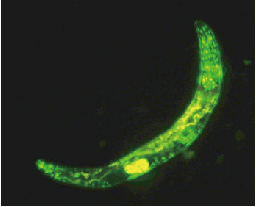
To identify a novel antibody with biological function, we rely on robust and effective screening methods. To fully utilize the power of the first generation phage display and the second generation intra-cellular combinatorial antibody library technologies, the lab has established a series of cellular assays based on function, morphology, and cell signaling pathways, for example the beta-lactamase reporter gene assay, the primary cell proliferation assay, the cancer cell proliferation sorting assay, and the myocardial cell toxicity assay. Living body is a complicated system and represents the next frontier for the combinatorial library technology. We are configuring a study model in c. elegans for the in vivo combinatorial antibody library approach. In addition, we are developing relevant murine models for the study of hepatocyte expansion and regeneration.
Alongside with the screening methods, we want to develop a series of informatics tools that can reproduce the experimental results, and eventually predict them. A combination of homology modeling, docking prediction and molecular dynamics simulation will be used to understand how antibodies and selected proteins interact. The aim is to provide an explanation of experimental results at the molecular level and eventually use rational design for select the correct antibody a priori. In order to set up and test the methodology, we will first analyze the effect of binding of antibodies to gap junction channels and to the acid sensic channels, aiming at finding specific blockers for these channels or to modify their permeation properties.
|