On August 26th, 2020, a team led by SIAIS Distinguished Adjunct Professor Lin Haifan published new findings in PNAS in an article entitled “PIWIL1 Promotes Gastric Cancer via a piRNA-Independent Mechanism”. These findings reveal a new function and action mechanism of PIWI proteins in oncogenesis, guiding the identification of PIWI inhibitors to cure cancer.

Precision medicine aims to cure cancer without affecting normal tissues. PIWI proteins, initially discovered in Prof. Lin Haifan’s lab for their essential function in germline development, execute their functions by partnering with PIWI-interacting RNA (piRNA), a class of small noncoding RNA. These proteins provide a rare opportunity for targeted therapy of cancer because they are normally not expressed or required in somatic tissues but gain expression in diverse types of cancers. Thus, inhibiting PIWI expression should stop cancer development without affecting normal body function.
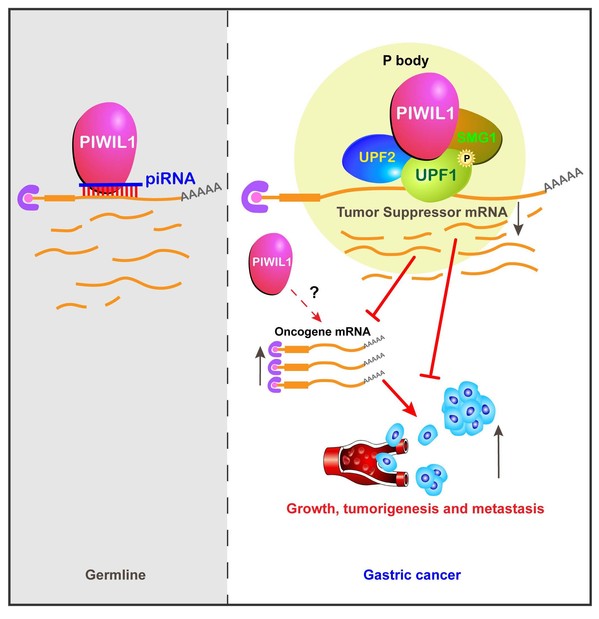
Here the team reported that PIWIL1, one of the four PIWI proteins in humans, is highly expressed in gastric cancer tissues and cell lines. Knocking out PIWIL1 gene (PIWIL1-KO) drastically reduces gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration, metastasis, and tumorigenesis. RNA deep sequencing of gastric cancer cell line SNU-1 revealed that KO significantly changes the transcriptome, causing the up-regulation of most of its associated transcripts. Moreover, the team reported the surprising finding that PIWIL1’s function in gastric cancer cells is independent of piRNA but rather involves the UPF1-mediated nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) mechanism. The findings revealed a novel function of PIWIL1 in cancer as well as a piRNA-independent mechanism underlying this function.
The findings bear three-fold significance:
(1) This is the first demonstration of the oncogenic function of PIWI proteins in gastric cancer.
(2) This is the first definitive demonstration of the piRNA-independent function of PIWI proteins.
(3) This is the first demonstration that Piwi proteins interact with the NMD mechanism to achieve its gene regulation function.
Shi Shuo, Research Assistant Professor from the SIAIS in ShanghaiTech University, is the first author of the research paper. Prof. Lin Haifan is the corresponding author. Yang Zhenzhen, Research Assistant Professor of SIAIS, Liu Sanhong, a former Research Associate Professor of SIAIS, and Yang Fan, Research Assistant of SIAIS, participated in the work. The paper’s first affiliation is ShanghaiTech University. All the computing work was performed at the ShanghaiTech High Performance Computing Platform.
Link for the article:
https://www.pnas.org/content/pnas/117/36/22390.full.pdf



