SIAIS Prof. Katsuhiko Mikoshiba with research team led by Prof. Hideki Nishitoh at Miyazaki University revealed a new mechanism of the brain atrophy regulated by ER chaperon Derlin which involves in cholesterol metabolism. published in iScience in July 23rd 2021.
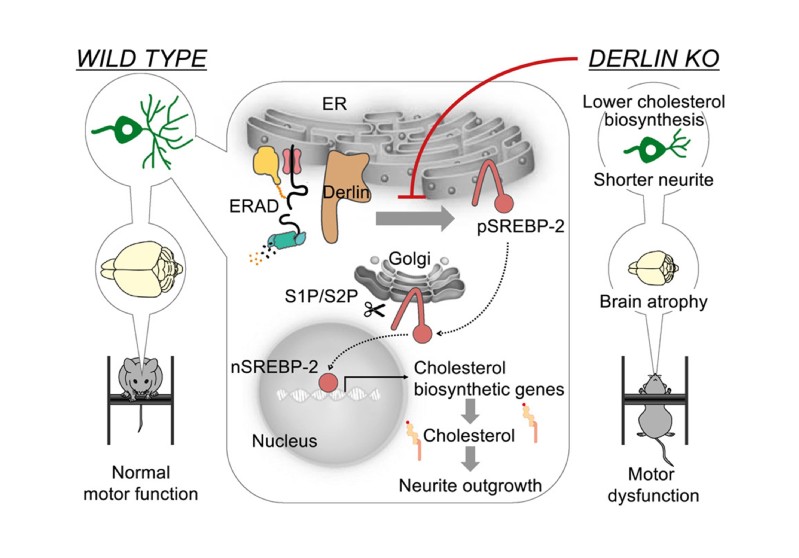
Cells degrade the unfolded proteins in order to prevent accumulation of misfolded proteins due to pathological endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Derlin as a member of ER-associated degradation (ERAD) complex eliminates the misfolded proteins for the quality control.
The research group discovered that Derlin promotes neurite outgrowth in vivo and in vitro and also promotes the brain development. They found Derlin knock out mice exhibit an atrophy of the cerebellum and striatum accompnied with motor control deficits.
Cholesterol biosynthesis is established to be essential for neural activity and many cholesterol biosynthetic enzyme genes are induced by the transcription factor SREBP-2 through Golgi apparatus.
Researchers found the Derlin knock out mice has low cholesterol amount in the brain and the SREBP-2 mediated brain cholesterol biosynthesis was inhibited,
They finally discovered that Derlin works as a component of Derlin-SREBP-2 pathway and plays an important role in a cholesterol synthesis in the brain.
The Derlin mediated cholesterol biosynthesis essential for neurite outgrowth was clearly confirmed by the observation that the reduced neurite outgrowth due to Derlin deficiency was rescued by SREBP-2 pathway activation.
Present findings demonstrate that the regulation of Derlins on the Derlins-SREBP-2 pathway and brain cholesterol biosynthesis are essential for postnatal brain development and its motor control giving us a clue for rescuing from brain atrophy.
First author: Takashi Sugiyama (there is no co-first author)
Corresponding author: Hidonori Ichijo, the University of Tokyo, Hideki Nishitoh Miyazaki University
iScience 24, 102758
July 23, 2021 a 2021 The Author(s). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2021.102758
Title: ERAD components Derlin-1 and Derlin-1 are essential for postnatal brain development and motor function.



